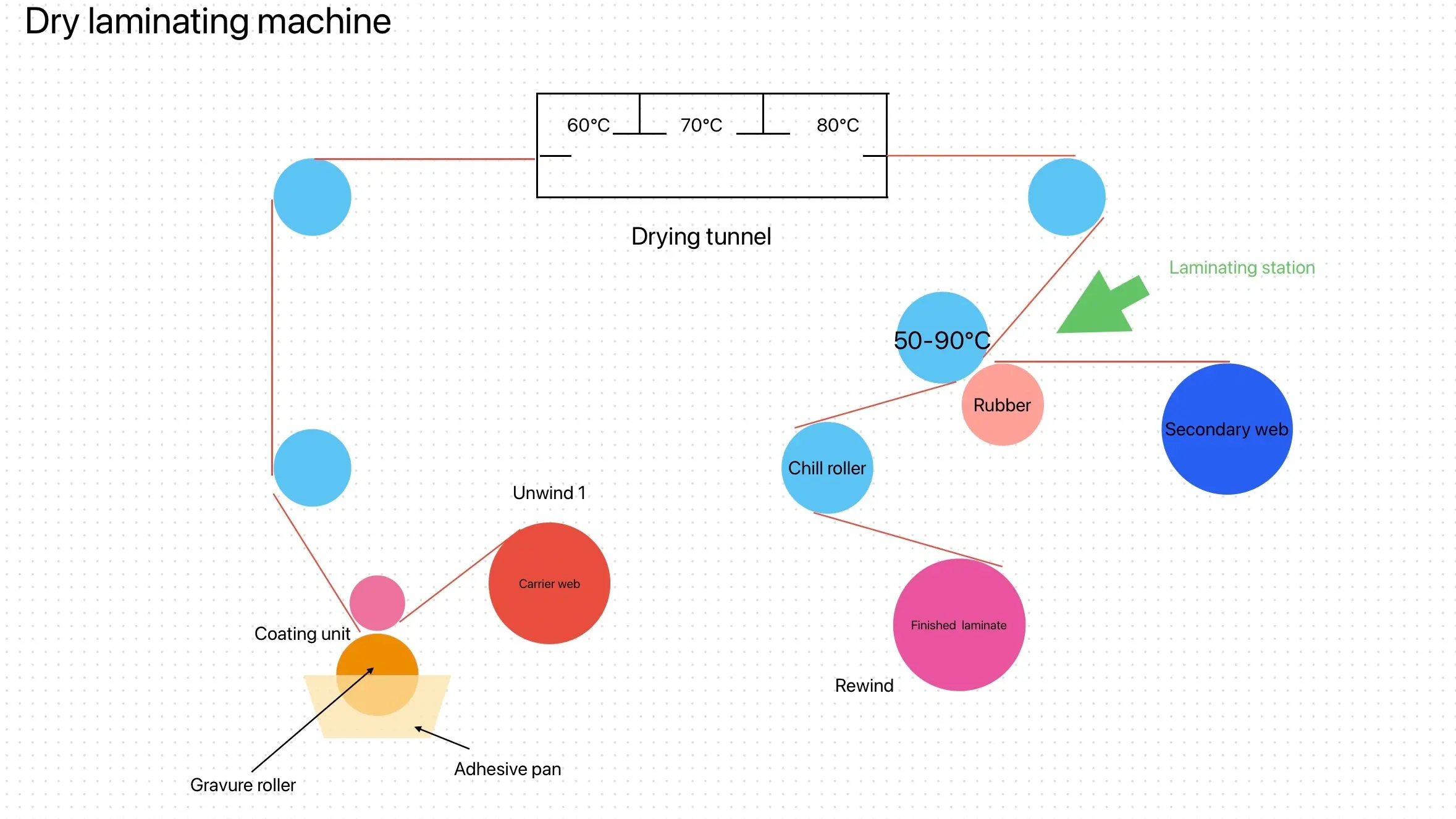
Traditional Hot Melt Bonds
The key difference between PUR hot melt and traditional hot melt lies in the type and strength of bond they create. Let’s start with traditional hot melt adhesives. Think of a traditional hot melt bond like a wax bond. The adhesive is heated to a liquid state, applied to the surfaces, and then allowed to cool and solidify. This process forms a temporary bond between the two substrates.
One of the key characteristics of traditional hot melt adhesives is that they are thermoplastic. This means that when you heat the bond, it reverts to a liquid state and can be easily separated. If you were to reheat the bonded parts, they would melt again, and the adhesive would lose its hold. While traditional hot melts can form strong bonds, their strength is limited by this reversibility and they don’t possess the long-term, durable adhesion that other types of adhesives, like PUR, offer.
In summary, traditional hot melt adhesives are quick and convenient for applications that require temporary or moderate adhesion strength, but they may not perform well in high-stress or long-lasting applications.

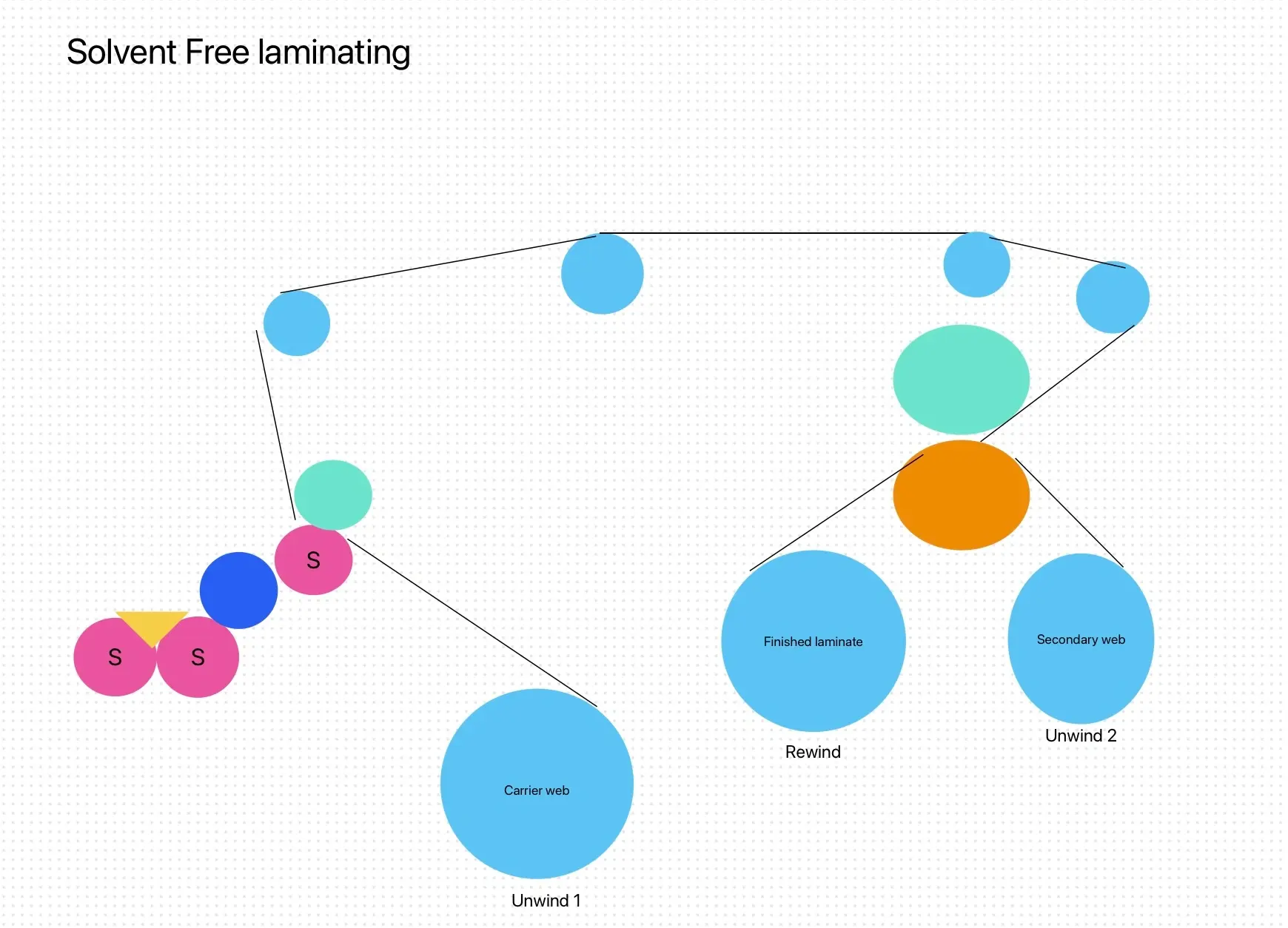
Polyurethane (PUR) Hot Melt Bonds
In contrast, PUR hot melt adhesives work on a fundamentally different chemistry. While PUR hot melt is also dispensed in a heated liquid form like traditional hot melt, the real magic happens as it cools and reacts with the moisture in the air. This reaction leads to a chemical change that significantly enhances the bond strength, creating a durable and permanent adhesive.
As the PUR adhesive cools, it forms a thermoset bond, which means the adhesive undergoes a chemical transformation that hardens it and makes the bond highly resistant to stress, heat, and moisture. Unlike thermoplastic adhesives, the bond created by PUR is not reversible when reheated, making it significantly stronger and more durable.
The curing process of PUR adhesives continues over a span of 24-48 hours, during which time the bond strengthens. This gives PUR hot melt its reputation for being incredibly robust, making it ideal for high-performance applications where long-term durability is critical, such as in the automotive, construction, and packaging industries.