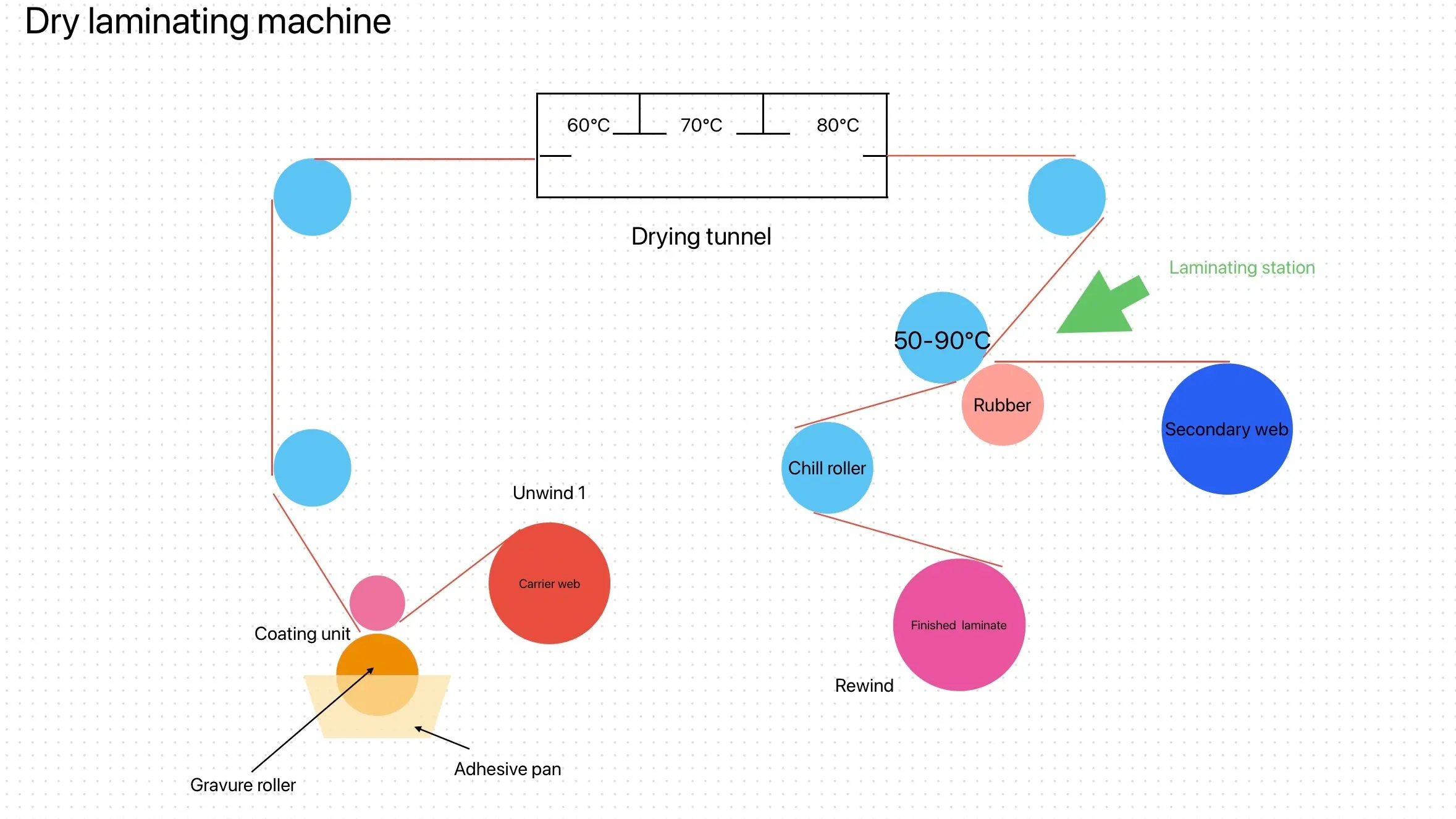
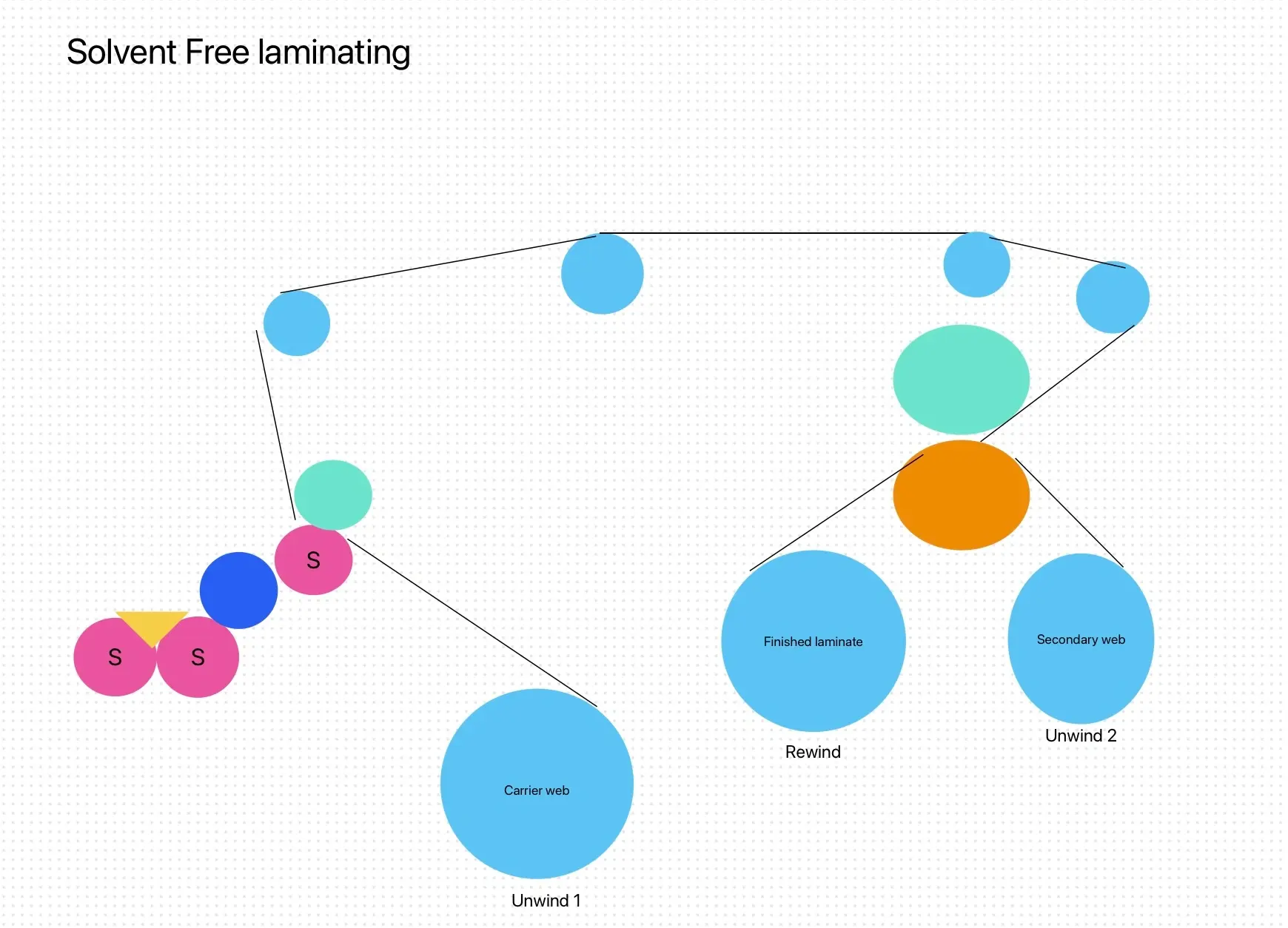
In the flexible packaging industry, lamination is a crucial process that enhances the functionality, durability, and aesthetic appeal of packaging materials. The choice of adhesive used in lamination significantly impacts the performance of the final product. This article explores the various types of lamination adhesives commonly used in flexible packaging, their characteristics, and their applications.

What is Lamination?
Lamination is a process where multiple layers of materials are bonded together using adhesives. This process not only provides structural integrity but also improves barrier properties, printability, and overall performance. In flexible packaging, lamination is essential for protecting contents from moisture, oxygen, light, and other environmental factors.
Types of Lamination Adhesives
Solvent-Based Adhesives
Composition: These adhesives are composed of polymer resins dissolved in organic solvents.
Characteristics: Solvent-based adhesives offer excellent adhesion and bonding strength. They are versatile and can be applied to a wide range of substrates.
Applications: Commonly used in high-performance applications such as food packaging, pharmaceutical products, and industrial materials. However, solvent evaporation during application can pose environmental concerns.
Water-Based Adhesives
Composition: These adhesives consist of polymer emulsions dispersed in water.
Characteristics: Water-based adhesives are eco-friendly, with low volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. They provide good adhesion and are user-friendly, making them suitable for various applications.
Applications: Commonly used in food packaging, labels, and flexible films. They are particularly advantageous for applications that require compliance with food safety regulations.
Hot Melt Adhesives
Composition: These adhesives are thermoplastic polymers that are applied in a molten state and solidify upon cooling.
Characteristics: Hot melt adhesives offer quick setting times and strong bond formation. They are easy to apply and do not require solvents or water.
Applications: Widely used in packaging applications such as snack foods, frozen foods, and personal care products. They are ideal for high-speed production lines due to their rapid curing time.
Reactive Adhesives
Composition: These adhesives cure through a chemical reaction, usually involving moisture or heat.
Characteristics: Reactive adhesives provide strong bonds and excellent resistance to temperature and humidity. They often have better performance in demanding environments.
Applications: Frequently used in specialized applications, such as medical packaging and heavy-duty industrial packaging, where durability is critical.
UV-Curable Adhesives
Composition: These adhesives contain photoinitiators that cure when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light.
Characteristics: UV-curable adhesives provide rapid curing and strong adhesion. They are known for their transparency and ability to bond a variety of substrates.
Applications: Ideal for applications that require a clear finish, such as graphics and decorative packaging, as well as certain food packaging solutions that benefit from fast production times.

Factors Influencing Adhesive Selection
When selecting the appropriate lamination adhesive, several factors must be considered:
Substrate Compatibility: The adhesive must be compatible with the materials being laminated, such as films, foils, and paper.
End-Use Requirements: Consider the specific requirements of the end product, including temperature resistance, moisture barrier properties, and chemical resistance.
Production Speed: The chosen adhesive should align with the production speed and techniques employed in the manufacturing process.
Environmental Regulations: Compliance with environmental standards and regulations is essential when selecting adhesives, particularly concerning VOC emissions.
Conclusion
The selection of lamination adhesives in the flexible packaging industry plays a pivotal role in ensuring product performance and sustainability. By understanding the different types of adhesives available—solvent-based, water-based, hot melt, reactive, and UV-curable—manufacturers can make informed decisions that enhance the quality and effectiveness of their packaging solutions. As the industry continues to evolve, the focus on eco-friendly and high-performance adhesives will drive innovation and improve outcomes for both manufacturers and consumers.